Part III of China's medical security system: bridging the urban-rural divide (2018-present)
The country is patching up the hurried transition to a market economy and striving towards the goal of common prosperity.
This is Jia Yuxuan from Beijing, finally coming to the present phase of China’s medical security system, after the planned economy era and the early days of reform and opening up. This article, authored by Cai Haiqing, former Director of Treatment Insurance, Jiangxi Province Healthcare Security Administration, was originally published in Chinese on the WeChat account Hailiao Qingtan海聊清谈. It was then reposted by China Health Insurance中国医疗保险, a mainstream magazine affiliated with the National Healthcare Security Administration of China.
In Part III of the article, Cai Haiqing examines the period from 2018 onward, highlighting how China's medical security system has increasingly focused on bridging the urban-rural divide and achieving common prosperity.
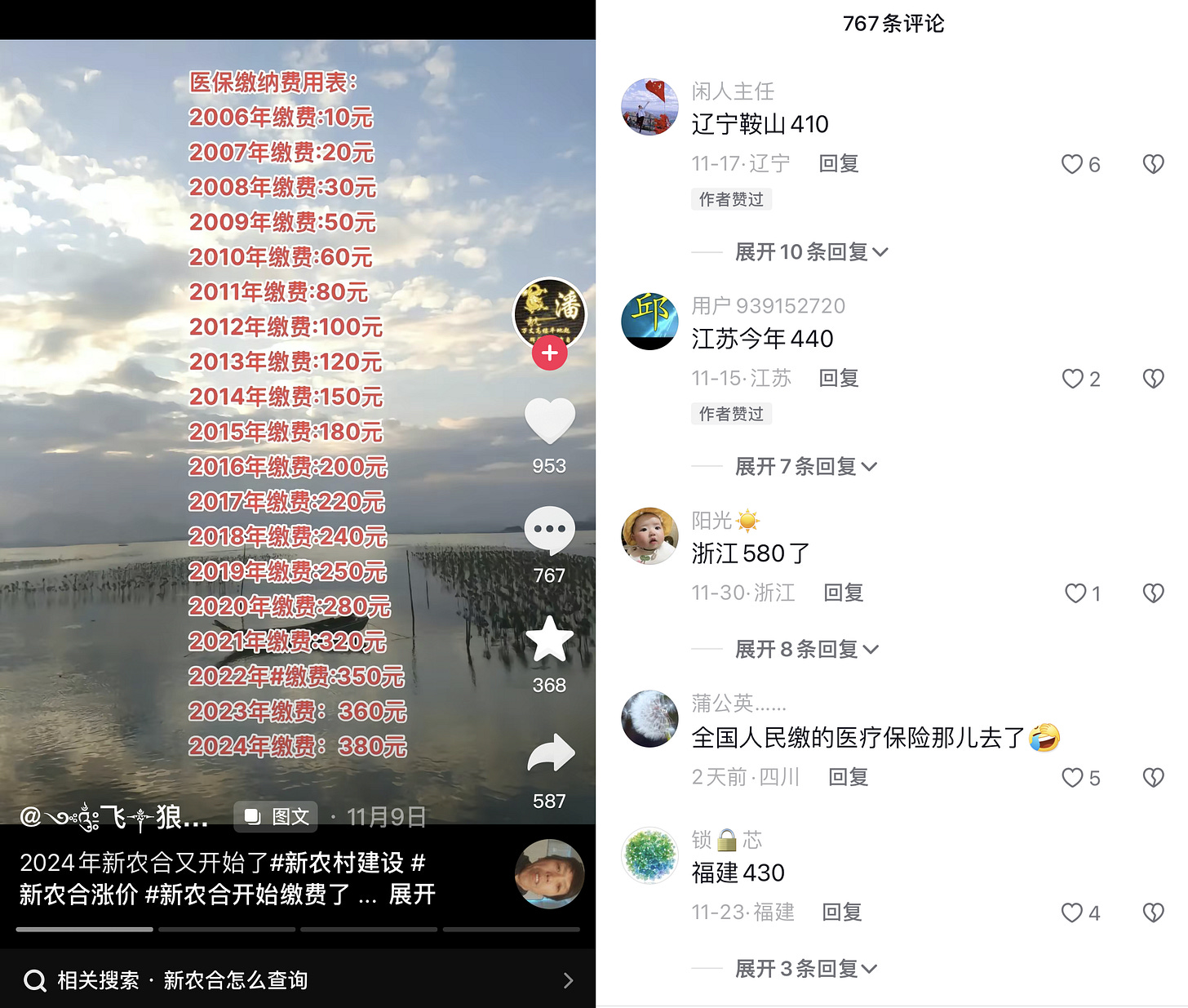
This policy goal is especially relevant these days as the New Rural Cooperative Medical Scheme (NCMS), highlighted in Part II of Cai Haiqing's article, begins a new contribution cycle. There have been rising grievances with the increasing contribution rates to the NCMS in recent years, which are growing at a rather disconcerting pace. This growing financial burden, especially for the lower-income families in rural areas, resulted in a significant drop in NCMS participation by 22 million in 2020. A popular Douyin (Chinese version of TikTok) video posted on Nov. 9, 2023, which displayed the escalating NCMS fees from 2006 to 2024, has prompted many users to share their personal complaints about these rising costs and express intentions to discontinue their NCMS memberships.
Building a Unified and Standardized Medical Security System Across Urban and Rural Areas
On May 31, 2018, the National Healthcare Security Administration (NHSA) was officially established, taking on the comprehensive responsibility of uniformly managing medical security affairs. This completely eliminated the institutional obstacles that had long restricted China's medical insurance reforms and development, paving the way and laying the foundation for the high-quality development of China's medical security undertakings.
Navigating Medical Insurance System Reforms through Top-Level Design
On February 25, 2020, the Party Central Committee and the State Council issued the "Opinions on Deepening the Reform of the Medical Security System" (hereinafter referred to as the "Opinions"). The Opinions addressed longstanding debates over institutional choices and reform approaches, clarifying the guiding ideologies, basic principles, development objectives, key reform tasks, developmental orientations, and corresponding action plans for comprehensively deepening China's medical security system reform. In doing so, it offered a scientific top-level design and systematic action guide for the comprehensive deepening of the medical security system reform.
On September 23, 2021, the "14th Five-Year Plan for Universal Medical Security" (hereinafter referred to as the "Plan") was officially released. This marked China's first five-year plan in the medical insurance field and served as a comprehensive reflection of the spirit of the Opinions. The Plan precisely outlines the roadmap for the high-quality development of medical security during the 14th Five-Year period, signifying China's entry into a new development phase aimed at fully establishing a high-quality and sustainable medical security system with distinctive Chinese characteristics.
Strengthening Institutional Reform for More Standardized and Unified Management and Services in Medical Security System
For a long time, China's medical insurance reforms primarily relied on policy documents for guidance. Due to regional fragmentation, countless policy documents were issued by various levels of government and their respective departments, resulting in a jumble of policies and measures. This not only weakened the standardization and uniformity of the medical security system but also intensified regional and urban-rural imbalances, hindering the sustainable development of the medical security system. Hence, the medical security system needs prompt reforms to achieve standardized and unified management and services.
To promote standardized management of the medical security system, on January 19, 2021, the NHSA and the Ministry of Finance jointly issued the "Opinions on Establishing a Medical Security Benefits List System" (hereinafter referred to as the "Benefits List"). The Benefits List elevated the authority to set and determine benefits to the state, further clarifying the institutional framework, main policy content, payment items and standards of BMI funds, and areas of non-payment, further solidifying the foundation for the development of the basic medical security system.
On January 15, 2021, the State Council introduced the first administrative regulation on China's medical security, titled the "Regulations on the Supervision and Management of the Use of Medical Security Funds." The enforcement of the Regulation establishes a legal foundation that ensures judicious and compliant utilization of medical insurance funds. It also facilitates effective supervision and management, providing a robust mechanism to safeguard the security of medical insurance funds.
Meanwhile, across the country, regions have diligently embraced the principles outlined in the Opinions by the Party Central Committee and the State Council. They are consistently raising the standard of medical insurance pooling, effectively achieving city-level pooling. Since 2020, various cities have sequentially introduced city-level pooling plans for BMI. Following trials in 2021 and full implementation in 2022, city-level pooling of the BMI fund has been essentially realized nationwide. This accomplishment ensures standardization and uniformity of the BMI system on a broader scale.
The gradual rise in the pooling level of BMI is effectively reducing the excessive regional fragmentation inherent in the current medical insurance system. This, in turn, helps eliminate adverse effects on fair treatment and mutual aid capabilities, representing another significant stride in the comprehensive deepening of medical insurance system reforms.
Modernizing Medical Security Governance with Standardized Management
In addressing the persistent challenges of regional fragmentation, departmental segmentation, and the absence of uniformity in medical insurance service standards, information sharing, system division, and regional isolation, the NHSA has made standardization and normalization of medical insurance a top priority.
On June 20, 2019, the NHSA issued the "Guidance on Medical Security Standardization Work", initiating the promotion of standardized construction for medical security. On September 23 of the same year, they released the "Coding Rules and Methods for Medical Security Designated Medical Institutions and Other Information", accelerating the promotion of a unified medical insurance information coding standard, forming a unified "common language" nationwide.
Since 2020, the NHSA has sequentially issued six administrative regulations, including the "Interim Measures for Basic Medical Insurance Medication Management", the "Interim Measures for the Management of Designated Medical Institutions for Medical Security", and others. These regulations provide a concrete institutional basis for transitioning medical insurance management services toward standardization.
Since 2020, the NHSA has successively promulgated six administrative regulations, including the "Interim Measures for the Management of Drugs in Basic Medical Insurance", the "Interim Measures for the Designated Management of Medical Institutions in Medical Insurance", the "Interim Measures for the Administration of Medical Insurance Designation for Retail Pharmacies", the "Interim Provisions on Administrative Penalties for Medical Insurance", the "Interim Measures for the Supervision and Management Reporting and Handling of the Use of Medical Insurance Funds", and the "Interim Measures for the Flight Inspection Management of Medical Insurance Funds". These six administrative regulations provide specific institutional guidance to streamline the management services in medical insurance operations.
To further enhance the quality of medical insurance management services and operational efficiency, continually improve the public's experience with medical insurance services, the NHSA has formulated a series of policy documents to meet the growing service demands of the people.
On April 30, 2020, the NHSA issued the "List of National Medical Security Administrative Service Items." This initiative is specifically designed to address vexing issues in the medical security sector concerning the public, with the goal of simplifying the service process through a one-stop handling approach for individuals' medical affairs. The overarching objective is to establish a unified and standardized national list of medical insurance administrative service items.
To address difficulties faced by groups such as the elderly in utilizing intelligent technology, on December 26, 2020, the NHSA issued the "Implementation Opinions on Adhering to the Parallel Optimization of Traditional Service Modes and Innovative Intelligent Services to Improve Medical Security Services". It explicitly called for improving traditional service methods while concurrently promoting the widespread use of intelligent technology, particularly among the elderly. The objective was to improve the adaptability of medical insurance services for the elderly by tackling issues such as cumbersome enrollment registration, limited applicability of online services for seniors, inconvenient manual reimbursement procedures, challenges in recording medical treatments across various locations, and the necessity for enhancing administrative service awareness and capabilities.
On July 16, 2021, the NHSA, in its document "Opinions on Optimizing Convenient Services in the Medical Insurance Field", specified several measures to enhance convenience in medical insurance services. These measures include promoting standardization and streamlining of services, advancing reforms for a more efficient "one-stop handling of affairs," and utilizing "Internet + medical insurance services." The efforts also aim to optimize processes like the transfer and continuation of medical insurance relationships, settlement of expenses for out-of-town treatments, and local handling of medical insurance services. Improvements in the management of agreements with designated medical institutions, service systems for medical insurance operations, and data support are part of these initiatives. Additionally, there's a focus on establishing exemplary service windows and combating fraud in the medical insurance field.
On May 25, 2023, the General Office of the NHSA released the "Notice on Implementing Sixteen Measures for Convenient Medical Insurance Services," which places a strong emphasis on simplifying procedures, minimizing documentation, shortening timelines, and innovating service models to enhance public convenience. This initiative aimed to address obstacles and challenges in medical insurance administrative services, implementing practical measures to maximize convenience for the public and continually enhance their sense of happiness, satisfaction, and security.
Main Features of the Comprehensive Deepening Phase of the Medical Security System Reform
During this phase, deepening reforms in the medical insurance system exhibited three distinctive features:
1) Direct Leadership
The initiative was propelled directly by the Party Central Committee and the State Council, departing from the past bottom-up exploratory approach and embracing a top-down unified promotion guided by top-level design.
2) Clear Objectives and Right Direction
Unlike the multifaceted experimentation without a clear direction in the past, the current phase witnessed the establishment of a comprehensive medical insurance system with Chinese characteristics. The approach adhered to the objective laws governing the medical insurance system, setting clear objectives and the right direction.
3) Benefits Beyond Reforms
The comprehensive deepening of medical insurance reforms transcended simple "add-ons." Instead, it predominantly focused on adjusting the existing structure and rectifying past institutional defects and imbalanced interest patterns. This strategy resulted in unlocking substantial benefits derived from the reform process.